
If the pupil fails to constrict, an undiluted pilocarpine solution is used. DiagnosisĪdie’s pupil can be identified by the constriction of a pupil with diluted pilocarpine drops. Non-pupil sparing (“surgical pupil”): posterior communicating artery aneurysm, uncal herniationĪ surgical pupil often requires urgent investigations with neurosurgical intervention (e.g.Pupil-sparing (“medical pupil”): diabetes mellitus, ischaemic stroke.Therefore, an oculomotor nerve palsy presents as a ‘ down and out’ gaze and ptosis, occasionally accompanied by mydriasis of the pupil.Ĭauses of an oculomotor nerve palsy can be split to: Additionally, the nerve provides parasympathetic innervation to the sphincter pupillae muscles of the iris which are involved in the constriction of the pupil. It also supplies the levator palpebrae superioris, which raises the upper eyelid. The oculomotor nerve supplies four of the six extraocular muscles, which are involved in the movement of the eye: superior rectus, medial rectus, inferior rectus and inferior oblique. The clinical findings in Adie’s pupil Oculomotor nerve palsy When associated with areflexia of the knee and/or ankles, this condition is known as Holmes-Adie’s syndrome. It is characterised by a poor or absent light reflex and an intact but slow accommodation reflex ( ‘light-near dissociation’). Pharmacological: atropine, tropicamide, MDMA, ecstasyĪdie’s pupil is a benign condition typically affecting young women, possibly secondary to viral or bacterial infection affecting the ciliary ganglion.This typically represents a disruption of the parasympathetic nervous system. Here, the abnormal pupil will be unable to constrict in the light and will appear dilated (mydriatic). CT chest for Pancoast tumour) and referral to specialist teams. The management of Horner’s syndrome depends on the underlying cause and the patient will require further investigation (e.g. Therefore, hydroxyamphetamine will correct a preganglionic Horner’s but will not work for postganglionic causes, where the anisocoria persists. Hydroxyamphetamine increases the release of noradrenaline at the synaptic cleft and requires a working postganglionic neuron to relay the action potential. The Paredrine test refers to using 1% hydroxyamphetamine eye drops to differentiate between preganglionic and postganglionic causes of Horner’s. Patients presenting with an acute history of Horner’s syndrome with neck pain and dysphagia require an urgent MRI neck to investigate for carotid artery dissection.Ī diagnosis of Horner’s can be confirmed by administering 0.5% apraclonidine (alpha-2 agonist) eye drops which will dilate the miotic pupil and correct the anisocoria. Postganglionic (no anhidrosis): carotid artery dissection, cavernous sinus thrombosis, cluster headaches.Preganglionic (anhidrosis of face): Pancoast tumour, thyroid mass, cervical rib.Central: stroke, multiple sclerosis, tumours.Horner’s syndrome is characterised by the triad of miosis, anhidrosis and ptosis (due to disruption to the sympathetic innervation of the Muller’s muscle).
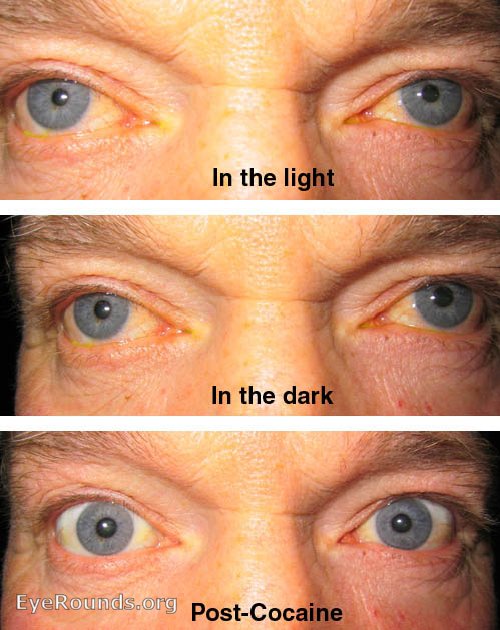
Pharmacological: pilocarpine, organophosphate insecticides.Mechanical: trauma, previous surgery, secondary to inflammation (anterior uveitis).Argyll-Robertson pupil: characteristic of neurosyphilis, seen usually as bilaterally constricted pupils that can accommodate but not react to light.These pupils typically represent a disruption of the sympathetic nervous system (e.g. The abnormal pupil can be identified by its failure to dilate in the dark thereby appearing constricted (miotic).
For more information, see the Geeky Medics guide to the examination of the eyes and vision. This should include checking accommodation and pupillary light reflexes, as well as slit-lamp examination. Therefore, assessment of the pupil should take place in both light and dark conditions. Pathological anisocoria can be identified by worsening anisocoria in either light or dark conditions. 2Ĭlinical examination should demonstrate a difference of less than 1mm between pupil size which typically remains the same in both light and dark conditions. Physiological anisocoria occurs in up to 20% of the population but the exact cause is unknown. You might also be interested in our medical flashcard collection which contains over 1000 flashcards that cover key medical topics.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
